By combining email security, web browsing protection, perimeter posture and awareness culture in one native solution, businesses can efficiently safeguard against phishing threats, bolstering resilience and future-proofing their systems.



Fraudulent tactics in your inbox can expose you to deceptive techniques that cybercriminals use to manipulate unsuspecting victims. Phishing involves deceiving recipients into disclosing sensitive information through seemingly legitimate emails. Spear-phishing raises the bar by crafting tailored messages based on the target’s business intel, while whaling impersonates high-level executives to deceive lower-level employees presenting the potential for financial losses.
Malicious websites are a significant threat in the digital landscape, as they are specifically designed to compromise user’s devices, steal sensitive data, or exploit system vulnerabilities. Industry best practices dictates the behavior of software should be transparent and not be deceptive, exfiltrative, unpredictive, and/or difficult to remove. Malware, lurking in malicious ads, lures users to deceptive websites or automatically download malware once clicked.
Social engineering is a psychological method used by cybercriminals to exploit human trust and gain access to sensitive information. A common form of social engineering is phishing attacks, where attackers impersonate trusted entities via email, text, or phone calls with the intent to deceive individuals into revealing personal data.
Exposed services, such as open ports, misconfigured firewalls, and applications with vulnerabilities, enable hackers to infiltrate networks. Missing records, such as incorrect DNS records, missing SPF or DKIM records, and other configuration errors, can lead to phishing attacks, spoofing, and more, while while leaked credentials, found in data dumps and other lists on the dark web and pose a critical risk to employees and businesses if unchecked.
Phishing emails are sent every day
Of data breaches occur as a result of phishing attacks
Of users cannot identify a sophisticated phishing email
CTS Cyber Threat Security continuously scans for all inbound traffic with advanced anti-phishing email protection solution
CTS initiates email detection through anti-phishing and anti-malware engines powered by AI.
CTS Cyber Threat Security monitors internet browsing to detect potential phishing attempts and delivers real-time alerts to system admins, enabling timely responses.
Utilizing cutting-edge generative AI, phishing simulation emails are crafted on the fly based on custom inputs, targeting groups of employees and reporting on pass/fail status.
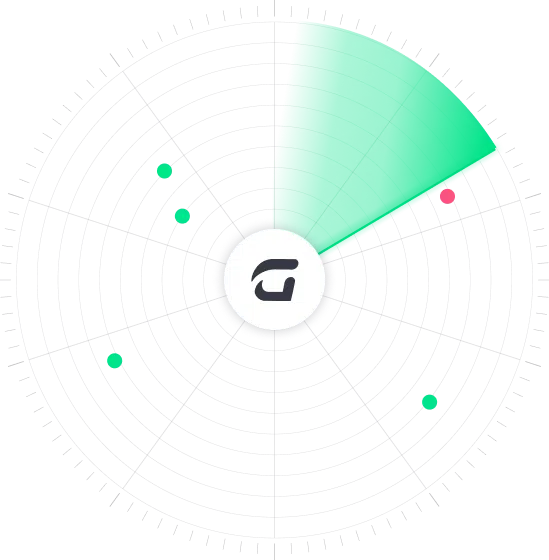
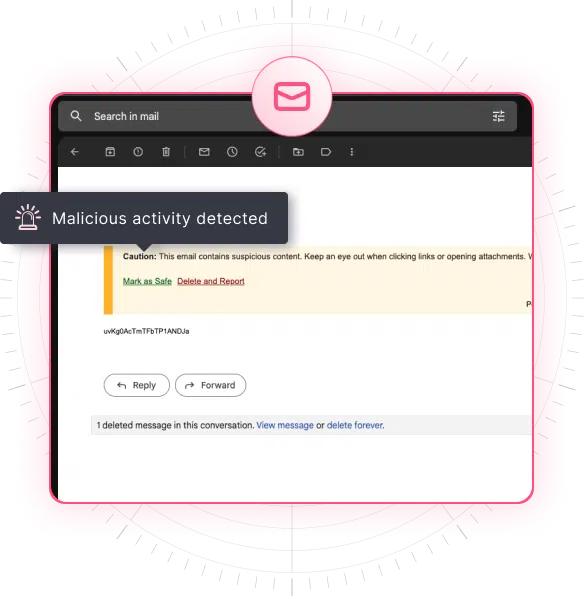
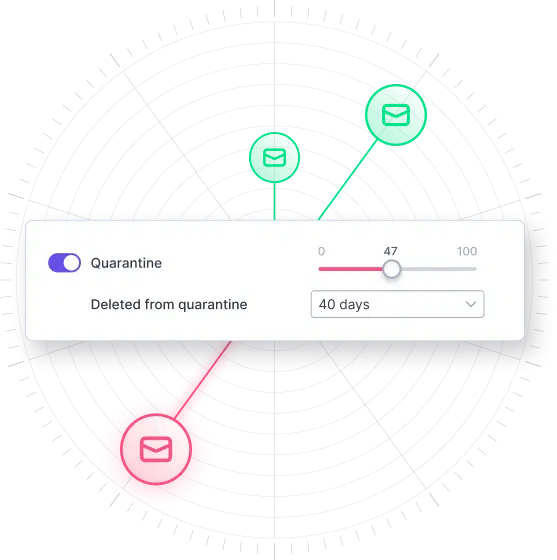

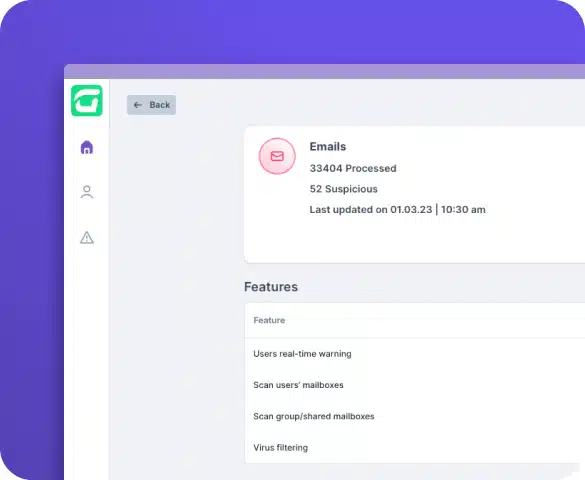
CTS Cyber Threat Security streamlines email protection with its fully managed, cloud-based solution that eliminates manual setup and seamlessly integrates with Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace accounts. Leveraging advanced predictive analysis, global intelligence tools, and continuous updates, CTS Cyber Threat Security provides robust defense against multiple attack vectors.
High-risk emails are immediately placed into quarantine to programmatically remove the threat. Employees receive immediate warnings and recommended actions for potentially harmful emails, while IT admins can automatically flag and remove malicious messages.
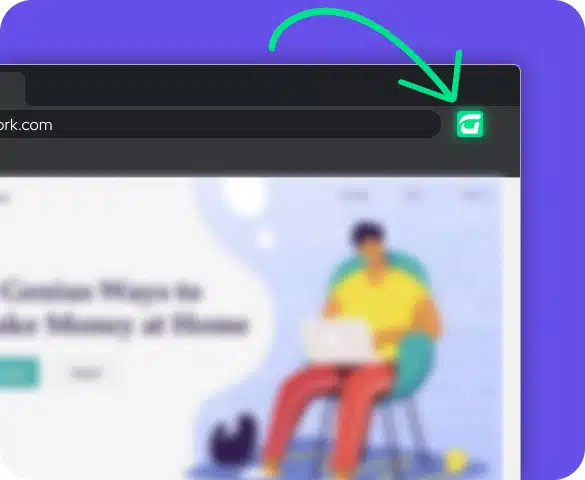
CTS Cyber Threat Security browser extension plays a vital role in safeguarding employees’ online security as they engage in their daily internet activities. Working seamlessly with the main platform, the extension actively monitors access to known malicious websites, web redirects to phishing sites, and continuously scans for unsafe browser extensions.
By offering real-time alerts and comprehensive website analysis, the CTS Cyber Threat Security browser extension empowers employees to make informed decisions and navigate the internet safely.
The CTS Cyber Threat Security external active risk monitoring offers an essential component to protect against phishing attacks by conducting an automatic external surface scan and dark web analysis. By assessing a business’s digital footprint, the solution identifies exposed services like missing DNS records (DKIM, DMARC, SPF), invalid chains of trust (TLS/SSL), leaked credentials, and potential business targeting.
CTS Cyber Threat Security ensures that employees’ and clients’ digital assets remain secure from targeted phishing attacks that take advantage of external vulnerabilities while preventing domain spoofing, hijacking or squatting that are key vectors for cybercriminal exploitation.
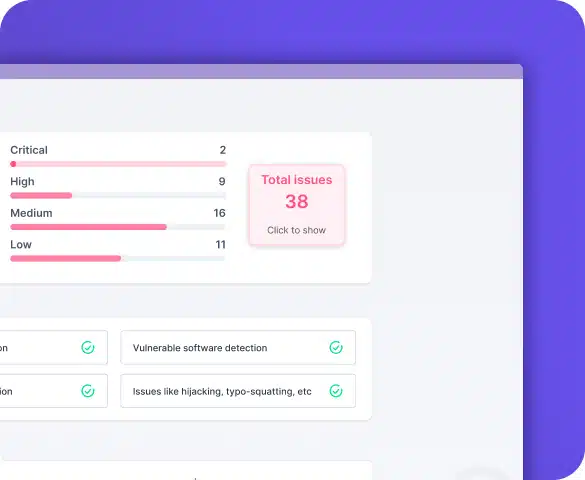
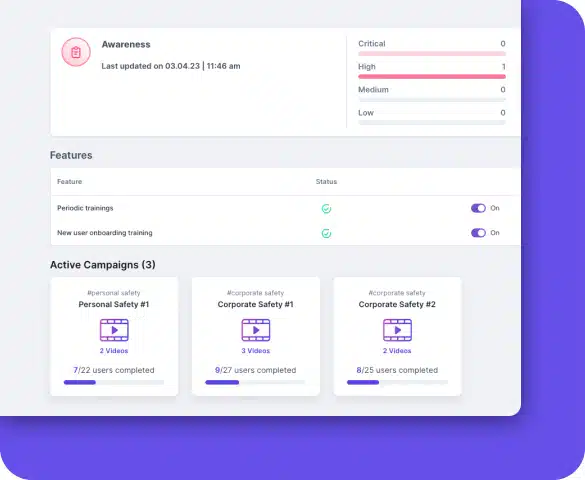
CTS Cyber Threat Security ensures up-to-date employee training by notifying admins of training status and recommending industry-standard best practices. Customizable campaign planning allows businesses to target specific users and meet company goals.
Phishing simulations help employees learn to avoid threats like ransomware and malware, while mandatory evaluations measure the impact of training.
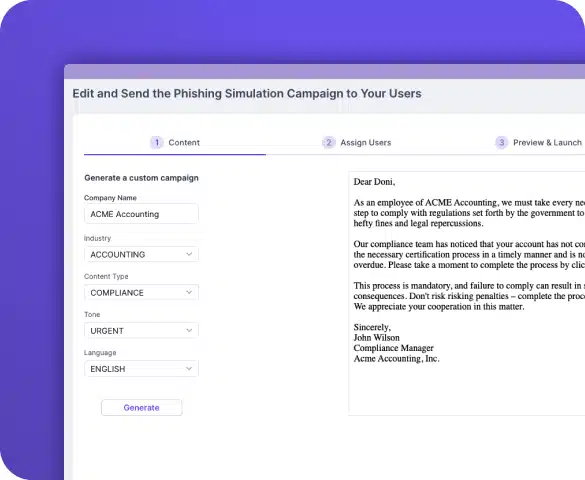
Leveraging generative AI, CTS Cyber Threat Security has moved beyond the static library approach, where users had to choose from a predefined list of emails. Now, our advanced technology enables you to generate custom content on the fly for each department based on unique guidelines.
The CTS Cyber Threat Security generative AI model is constantly trained and updated with the latest information on real-world phishing attacks, ensuring highly accurate simulations. This seamless approach ensures employees are aware and well-equipped to handle emerging threats.
While email filters can significantly reduce the amount of phishing emails you receive, you cannot solely rely on them to completely protect you as sophisticated phishing attacks can often bypass traditional filters; it’s crucial to remain vigilant and practice good email hygiene to fully safeguard yourself against phishing attempts
If you receive a phishing email, do not click on any links, open attachments, or reply to the sender; instead, immediately delete the email and mark it as spam to protect yourself from potential harm. You can also report the phishing email to your IT department or the appropriate anti-phishing organization to help prevent others from falling victim to the same scam.
Yes, training programs can significantly help organizations strengthen their phishing protection by educating employees on how to identify and report phishing attempts, effectively creating a “human firewall” that can significantly reduce the risk of cyberattacks by raising awareness and teaching users to spot common phishing tactics; this makes them a crucial component of any robust cybersecurity strategy.
When you respond, you confirm that your email account is active, making you a target for further attacks. Your email security tools might then recognize the attacker as someone you trust, allowing future phishing attempts to land directly in your inbox.
a type of online scam that targets consumers by sending them an e-mail that appears to be from a well-known source – an internet service provider, a bank, or a mortgage company, for example. It asks the consumer to provide personal identifying information.
A whaling attack is a type of phishing attack where a particularly important person in the organization is targeted. It hinges on the cyber-criminal pretending to be a senior member of the organization to gain the trust of the intended target.
a type of phishing attack that targets a specific individual, group or organization. These personalized scams trick victims into divulging sensitive data, downloading malware or sending money to an attacker

